Tachometer Challenge
Overview
In this challenge you will measure the speed of a motor using a magnet, hall effect sensor and oscilloscope. Placing a magnet on the shaft of a motor, the hall effect will detect every time the shaft turns one revolution. Using an oscilloscope, you can measure the time it takes for each revolution.
Exercise:
Complete the exercise (Hall Effect Sensors) described above.
Find a motor in the back room. The motor should have no gear reduction. If you don’t know what this means, you can ask your teacher.
Determine the correct voltage for driving the motor. If it is not listed on the motor bin or on the motor itself, look up the motors part number (listed on motor). If this fails, assume the motor runs at 6V.
Connect the motor directly to a power supply using test leads and confirm that it spins at the correct voltage.
Make (or find) a three-wire extension that is more than 6-inches in length. The extension should have a three pin header on each end. This will allow you to move your hall effect sensor off the breadboard.
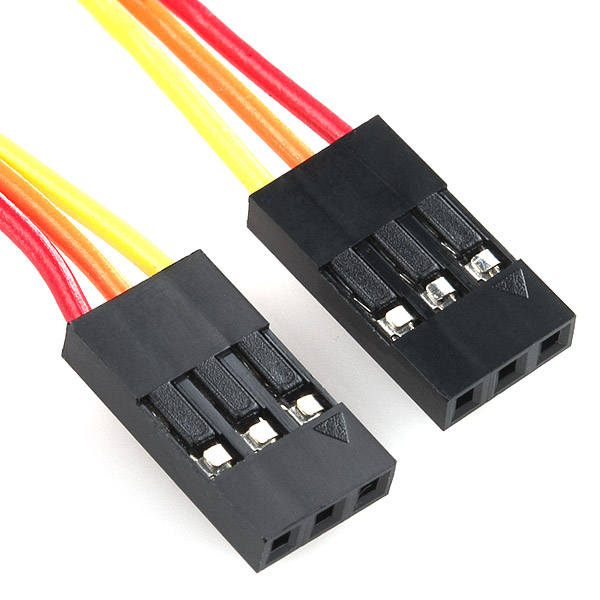

Place the hall effect sensor in one end of the cable and place the other end in the breadboard, in the same place where you had your sensor.
Set up your oscilloscope to read the output of the hall effect sensor. The ground lead should be connected to ground and the signal lead should be connected to the output of the hall effect sensor.
Turn on the motor.
Place the hall effect sensor near the spinning magnet until you begin to see evenly spaced pulses on your oscilloscope.
Adjust the TIME/DIV so that you easily see only one or two complete pulses on the screen. Note that a complete pulse is comprised of one high cycle and one low cycle. Complete the following.
Time between each horizontal division: ________
Number of divisions for each complete cycle: ________
Total time for each complete cycle: ________
Calculated frequency (the inverse of the total time): ________
Frequency reported by scope: ________
Calculate revolutions per minute (RPM). The speed of motors is most commonly measured in RPM. On your own, using the information you have collected to calculate RPM. Show your work below.